The Monopolistically Competitive Firm Shown in the Figure
When the monopolistically competitive firm shown in the above figure is at its long-run equilibrium it will be A producing the efficient scale of output and is at point A on the ATC curve. B producing more than the efficient scale of out-put and is at point C on the ATC curve.

Econ 212 Micro Chapter 13 Quiz Flashcards Quizlet
Monopolistic Competition Entry and Exit.
. When the monopolistically competitive firm shown in the above figure is at its long-run equilibrium it will be A producing the efficient scale of output and is at point A on the ATC curve. Based on the figure above the monopolistically competitive firm illustrated could infer that over the long run a. Refer to the diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm in short-runequilibrium.
Is in long-run equilibrium. Consider the diagram below depicting the revenue and cost conditions faced by a monopolistically competitive firm and then answer the following questions. This is clear because if you follow the dotted line above Q 0 you can see that price is above average cost.
Cannot operate profitably in the short run. A At P 0 and Q 0 the monopolistically competitive firm shown in this figure is making a positive economic profit. B producing more than the efficient scale of out-put and is at point C on the ATC curve.
This is clear because if you follow the dotted line above Q0 you can see that price is above average cost. In the long run purely competitive firms and monopolistically competitive firms earn zero economic profits while pure monopolies may or may not earn economic profits. Positive economic profits attract competing firms to the industry driving the original firms demand down to D 1.
Positive economic profits attract competing firms to the industry driving the original firms demand down to D 1. Might realize an economic profit or a. B producing more than the efficient scale of.
C total revenue is at a maximum. Total profit per week equals 120 times 2150 or 2580. MC ATC D 0 MR Quantity The monopolistically competitive firm shown in the figure Multiple Choice cannot operate profitably in the short run.
The above figure shows the demand and cost curves for a firm in monopolistic competition. When the monopolistically competitive firm shown in the above figure is at its long-run equilibrium it will be A producing the efficient scale of output and is at point A on the ATC curve. The monopolistically competitive firm shown in the figure might realize an economic profit or a loss depending on its choice of output level.
Some existing firms will leave the industry. The price of the product is 90. Can realize an economic profit.
The graph shows that. Monopolistic Competition Entry and Exit a At P0 and Q0 the monopolistically competitive firm shown in this figure is making a positive economic profit. The profit-maximizing price is-2500.
It is shown by the shaded rectangle. Refer to the graph shown of a monopolistically competitive firm. 5 The monopolistically competitive firm shown in the figure.
Positive economic profits attract competing firms to the industry driving the. They can maintain profit share without pursuing any innovation or product improvement. Existing firms would exit the industry which would increase their profit.
Asked Sep 2 2019 in Economics by livdinome. This is clear because if you follow the dotted line above Q 0 you can see that price is above average cost. A monopolistically competitive firm perceives a demand for its goods that is an intermediate case between monopoly and competition.
A At P 0 and Q 0 the monopolistically competitive firm shown in this figure is making a positive economic profit. The graph shows that. Is in long-run equilibrium.
The monopolistically competitive restaurant shown in the figure above responds to the arrival of immigrants by Price cost marginal revenue MC ATC PMC ATCMC PMC ATCMC DMC DMC MRMC MRMC QMC QMC Quantity A. According to the diagram the profit-maximizing output level is-25 units. A At P 0 and Q 0 the monopolistically competitive firm shown in this figure is making a positive economic profit.
When the monopolistically competitive firm shown in the above figure is at its long-run equilibrium it will be. New firms will enter the industry. Figure 102 offers a reminder that the demand curve as faced by a perfectly competitive firm is perfectly elastic or flat because the perfectly competitive firm can sell any quantity it wishes at the prevailing market price.
Because a monopolistically competitive firm faces a downward-sloping demand curve its marginal revenue curve is a downward-sloping line that lies below the demand curve as in the monopoly model. This is clear because if you follow the dotted line above Q 0 you can see that price is above average cost. Demand for their product will increase.
-30 units-40 units-45 units. Can realize an economic profit. In the figure the firm makes an economic profit of 40.
Using graphs similar to Figure 81 Short. 4 _______ A marginal revenue equals marginal cost. Lowering its price thereby.
This firms profit-maximizing price will be. D average costs are at a minimum. 5 _______ A might realize an.
Raising its price thereby diminishing the real purchasing power of the local population. 4 The monopolistically competitive seller maximizes profit by producing at the point where. B price equals marginal cost.
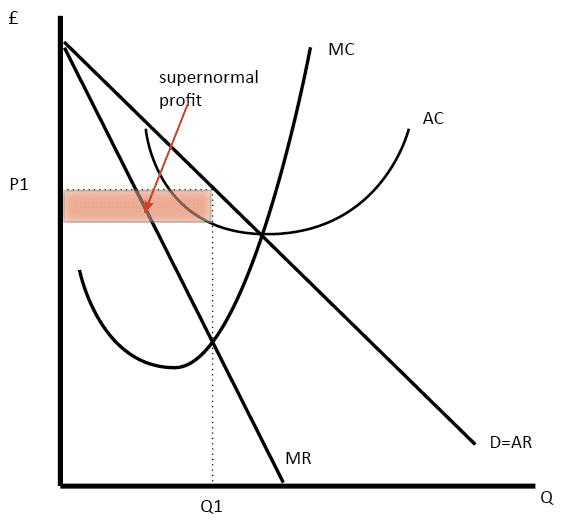
Monopolistic Competition Definition Diagram And Examples Economics Help

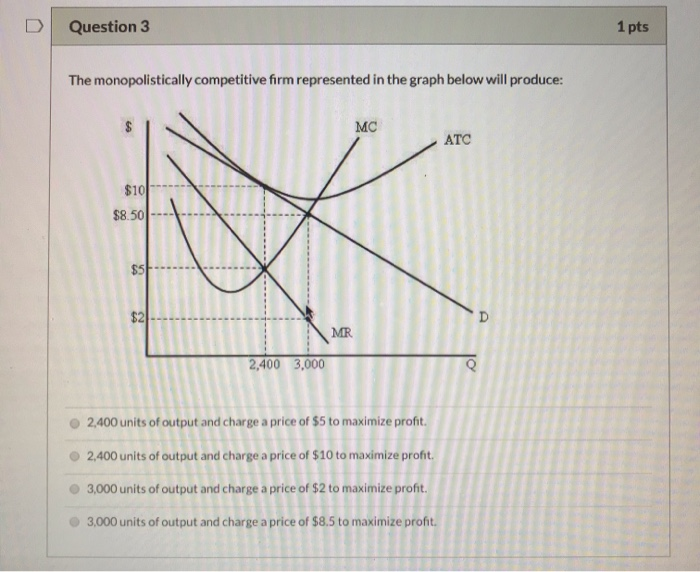
Solved Question 3 1 Pts The Monopolistically Competitive Chegg Com
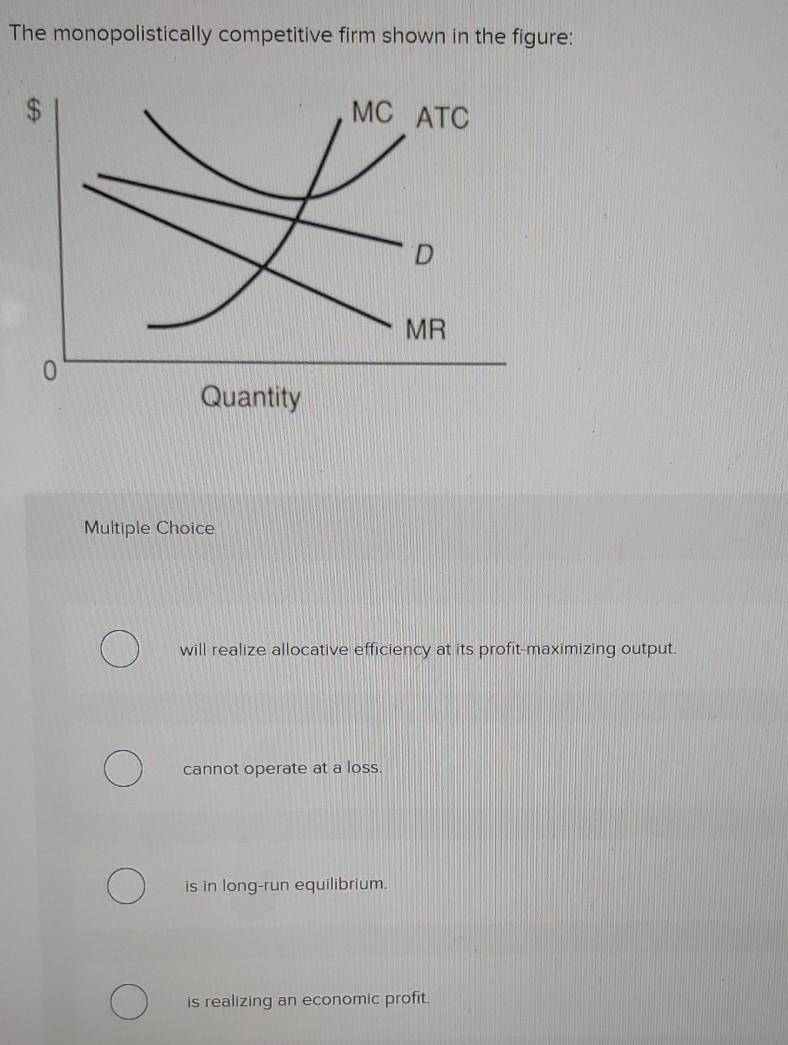
Solved The Monopolistically Competitive Firm Shown In The Chegg Com
No comments for "The Monopolistically Competitive Firm Shown in the Figure"
Post a Comment